Web technology has revolutionized the way we interact with the digital world. From the simplest websites to complex applications, the backbone of today’s internet is built upon various web technologies that allow developers to create dynamic, interactive, and responsive platforms. As we dive deeper into the technological advancements shaping the future, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of web technology, its evolution, and its applications in the current digital era.
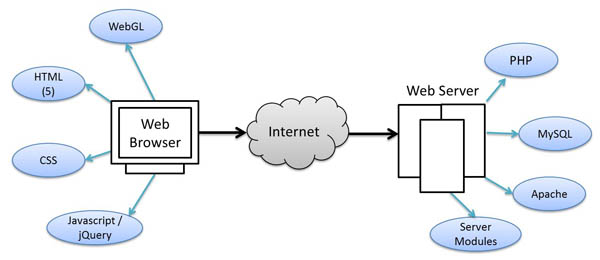
Web technology refers to the tools and techniques used to communicate between different types of devices over the internet. These technologies enable websites and web applications to function smoothly, ensuring users can access content efficiently. It encompasses a wide range of technologies including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Web servers, and more.
At its core, web technology allows the seamless interaction between the user’s device and a web server, resulting in the display of information in the form of web pages or applications. Every click, form submission, and interaction on a website is powered by web technologies working together in harmony.
Web technology has evolved dramatically since the inception of the internet. Here’s a brief look at its major milestones:
Web 1.0: The earliest phase of the internet, Web 1.0, was static and limited to text-based content. Websites were simple HTML pages with little to no interactivity. Users could only consume information without contributing or interacting with the content.
Web 2.0: This phase introduced interactivity and user-generated content. Platforms like YouTube, Facebook, and Wikipedia allowed users to create and share content, marking the beginning of the social web. Web 2.0 also introduced JavaScript and CSS to enable dynamic content and improved design.
Web 3.0: Also known as the semantic web, Web 3.0 focuses on creating more intelligent and personalized experiences. It uses technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain to enhance data analysis, security, and user interaction.
Web 4.0: The future of web technology is likely to involve more advanced AI, automation, and real-time interactions. Concepts like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Augmented Reality (AR) will likely dominate this phase.
Web technology can be broadly classified into frontend and backend technologies. Let's break down the most commonly used tools:
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is the foundation of all web pages. It defines the structure of content on the web, using various tags to display headings, paragraphs, images, and more. HTML ensures that text, images, and links appear correctly on web browsers.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): While HTML structures the content, CSS styles it. CSS controls the layout, colors, fonts, and overall appearance of a website. It enables web developers to create visually appealing websites that are responsive to different devices.
JavaScript: JavaScript brings websites to life by enabling interactivity. It allows developers to create dynamic web elements like sliders, animations, and interactive forms. JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js have further revolutionized frontend development, enabling more efficient coding and faster load times.
Web Servers: A web server stores the website's data and delivers it to the user's device upon request. Popular web servers include Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft IIS. The efficiency of a web server plays a crucial role in determining the speed and reliability of a website.
Databases: Websites need to store, retrieve, and manage large amounts of data. This is where databases come in. Popular databases used in web technology include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Oracle. These databases store data in an organized manner and allow websites to access user information, product details, and more.
Server-Side Languages: The server-side languages handle the logic behind a website's functionality. These languages interact with databases, manage requests from the frontend, and ensure that the backend processes run smoothly. Popular server-side languages include PHP, Python, Ruby, Node.js, and Java.
APIs play a pivotal role in web development by allowing applications to communicate with each other. They enable developers to integrate external services and functionalities into their web applications. For example, a website might use an API to integrate Google Maps for location-based services or a payment gateway for online transactions.
With the increasing use of mobile devices to access the internet, responsive web design has become a necessity. A responsive design ensures that websites are optimized for all screen sizes, whether accessed on a desktop, tablet, or smartphone.
To achieve responsiveness, web developers use techniques like media queries in CSS to adjust the layout of a webpage according to the screen size. The rise of progressive web apps (PWAs) has also transformed the way we build and experience websites. PWAs combine the best features of websites and mobile apps, offering faster load times and offline functionality.
As more businesses and individuals move online, the importance of web security has grown exponentially. From protecting sensitive user data to preventing cyberattacks, developers must implement robust security protocols. Common security measures include:
SSL Certificates: Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates encrypt the data transferred between a user's browser and a web server, ensuring privacy and security.
Authentication & Authorization: Websites often require user authentication (such as login systems) to access certain features. Authorization ensures that users only access the data and services they’re allowed to.
Firewalls: Web application firewalls (WAF) protect websites from common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
The world of web technology is ever-evolving. Here are some key trends shaping the future of web development:
AI-Powered Websites: Artificial intelligence is being integrated into web development to create more personalized user experiences. AI can be used to analyze user behavior and recommend content or products based on their preferences.
Voice Search Optimization: With the rise of smart speakers and virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, websites must now be optimized for voice search queries.
Motion UI: Web developers are increasingly using motion design elements like transitions, animations, and parallax scrolling to engage users and improve the overall user experience.
Single Page Applications (SPAs): SPAs like Gmail and Trello load a single HTML page and dynamically update the content as the user interacts with the application. This improves performance and provides a smoother user experience.
Web technology continues to evolve, shaping the way we interact with the digital world. From basic HTML websites to AI-powered platforms, the scope of web development has expanded significantly. Whether you are a business owner or a developer, staying updated with the latest web technologies is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today's digital landscape.