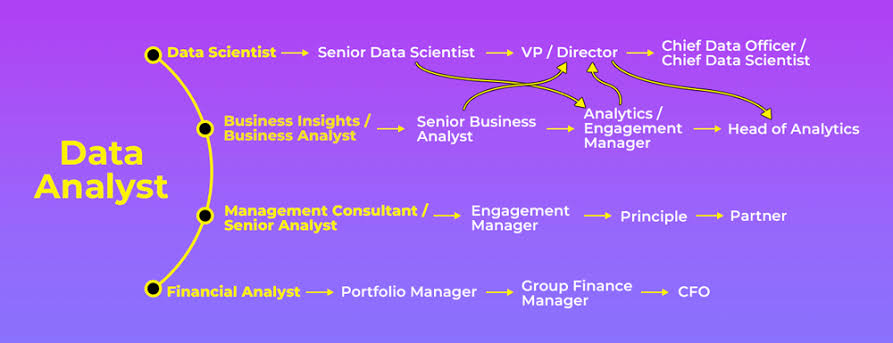
Introduction to Data Analysis
In the digital age, data is a critical asset for businesses. The role of a data analyst has
become indispensable in interpreting this vast amount of data to make informed
decisions. A data analyst is responsible for gathering, processing, and performing
statistical analyses on data. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential
steps and skills required to excel in the field of data analysis.
Understanding the Data Analyst Role
A data analyst's primary objective is to use data to extract actionable insights. This involves various tasks such as data cleaning, data visualization, and statistical analysis. Data
analysts work closely with stakeholders to understand their data needs and deliver
insights that help drive strategic decisions.
Educational Background and Key Skills
Educational Requirements
Most data analysts have a background in mathematics, statistics, computer science, or a
related field. A bachelor's degree is often the minimum requirement, though many
professionals further their education with master's degrees or specialized certifications.
Essential Skills for Data Analysts
1. Statistical Analysis: Understanding and applying statistical methods is crucial for
interpreting data accurately.
2. Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages such as Python, R, and SQL is
essential for data manipulation and analysis.
3. Data Visualization: Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Matplotlib help in creating visual
representations of data to communicate findings effectively.
4. Critical Thinking: Ability to think critically about data and derive meaningful insights.
5. Communication Skills: Explaining complex data insights in a clear and understandable manner to non-technical stakeholders.
Steps to Becoming a Data Analyst
1. Building a Strong Foundation
Start with a solid understanding of mathematics and statistics. Online courses, university degrees, and self-study can provide a good foundation. Focus on areas such as
probability, linear algebra, and calculus.
2. Learning Programming Languages
Familiarize yourself with essential programming languages:
- Python: Widely used for its versatility and extensive libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and
Scikit-Learn.
- R: Preferred for statistical analysis and data visualization.
- SQL: Essential for database management and manipulation.
3. Gaining Practical Experience
Hands-on experience is crucial. Engage in projects that involve real-world data sets.
Platforms like Kaggle offer competitions and datasets for practice. Building a portfolio
showcasing your work can be very beneficial.
4. Mastering Data Visualization Tools
Learn how to use data visualization tools to present your findings effectively:
- Tableau: Known for its powerful and flexible data visualization capabilities.
- Power BI: A Microsoft tool that integrates well with other Microsoft products.
- Matplotlib: A plotting library for the Python programming language and its numerical
mathematics extension NumPy.
5. Understanding Business Context
Having a good grasp of the business context is important. Understand the industry you are working in and how data can solve business problems. This will help you tailor your
analyses to meet business needs.
Advanced Data Analysis Techniques
1. Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is increasingly becoming a valuable skill for data analysts. It involves training algorithms to recognize patterns and make predictions. Familiarize yourself with
ML libraries such as Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow.
2. Big Data Technologies
Understanding big data technologies like Hadoop and Spark is beneficial as data volumes grow. These tools help in processing large datasets efficiently.
3. Data Warehousing
Knowledge of data warehousing solutions like Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and
Snowflake can be crucial for managing and querying large datasets.
4. Statistical Software
Proficiency in statistical software like SAS and SPSS can be advantageous, especially in
industries where these tools are standard.
Building a Portfolio and Networking
1. Creating a Portfolio
Your portfolio should include a variety of projects that showcase your skills. Include:
- Data cleaning and preprocessing tasks.
- Exploratory data analysis (EDA).
- Data visualization examples.
- Machine learning projects (if applicable).
2. Networking Networking is key to advancing your career. Join professional groups, attend industry
conferences, and participate in online forums. LinkedIn can be a powerful tool for
connecting with other professionals and finding job opportunities.
Certifications and Continuous Learning
1. Pursuing Certifications
Certifications can validate your skills and increase your marketability. Consider
certifications such as:
- Certified Data Professional (CDP)
- Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate
- Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
2. Staying Updated
The field of data analysis is constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest trends and
technologies by following industry blogs, attending webinars, and taking advanced
courses.
Conclusion
Becoming a data analyst requires a combination of technical skills, business acumen, and continuous learning. By following this comprehensive roadmap, you can develop the
expertise needed to excel in this dynamic and rewarding field. Remember, the journey to
becoming a proficient data analyst is ongoing, so keep learning and adapting to new
challenges and technologies..
 Best Mobile App Development Company in Delhi NCR | Oprezo India
Best Mobile App Development Company in Delhi NCR | Oprezo India
 Top Web Development Services in Delhi/NCR | Oprezo India – React JS, Angular JS, eCommerce & More
Top Web Development Services in Delhi/NCR | Oprezo India – React JS, Angular JS, eCommerce & More
 Top Mobile App Development Company in Delhi / NCR | Oprezo India
Top Mobile App Development Company in Delhi / NCR | Oprezo India
 Mobile App Development in Delhi - Android, iOS, Hybrid & Flutter | Oprezo India
Mobile App Development in Delhi - Android, iOS, Hybrid & Flutter | Oprezo India
 Why Oprezo India is the Best Web Development Partner in Delhi NCR?
Why Oprezo India is the Best Web Development Partner in Delhi NCR?